Modern applications of computer vision models in various sectors of the economy
Innovative research allows us to create AI solutions that exceed expectations, providing our clients with a competitive advantage and the security of their business
Computer vision, a field of artificial intelligence that enables machines to "see" and interpret visual information, is rapidly advancing. Continuous improvements in deep neural networks and large amounts of data have opened up new horizons for modern computer vision models. Let's consider how these achievements are applied in various sectors of the economy, transforming them.
Image Classification
The most basic task of computer vision is image classification. The goal here is to determine which class the presented image belongs to. For example, when analyzing a photo, a computer vision model can determine that it depicts a cat, not a dog or a bicycle. This task is achieved using neural networks such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) or architectures like Visual Transformers (ViT), which are trained on large datasets consisting of labeled class images.
Object Detection
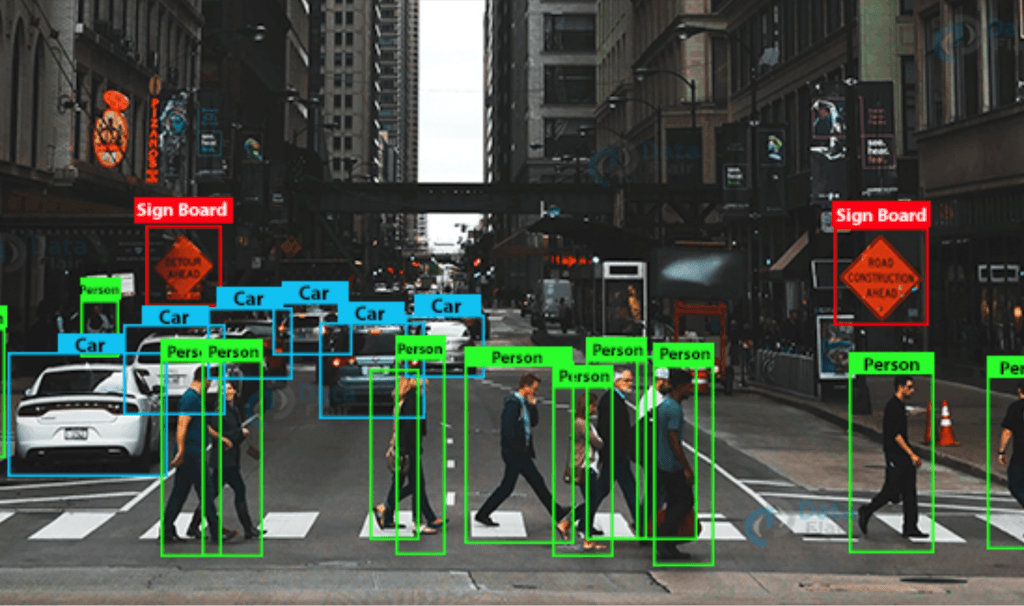
Object detection goes beyond classification. It not only identifies that there is an object of a certain class in the image, but also indicates its exact location using bounding boxes. For example, a detection model will not only say that there is a car in the image, but will also specify exactly where it is located. Popular algorithms for this task include YOLO (You Only Look Once) and DeTR.
Image Segmentation
Image segmentation is the task in which each pixel of the image is classified according to its label. It can be of two types: semantic segmentation, which identifies all pixels belonging to one class, and instance segmentation, which also distinguishes individual instances of the same class. For example, in an image with several people, an instance segmentation model can distinguish them from each other, while semantic segmentation will highlight all people in the same color. One of the leaders in this field is the Segment Anything (SAM) architecture.
Image Restoration and Inpainting
Image restoration involves reconstructing damaged or missing parts of an image. For example, using inpainting, old photos can fill in the gaps or unwanted objects can be removed from snapshots. Neural networks, especially GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks) and specific algorithms such as Diffusion Neural Networks, have made significant advances in this task.
Image Prediction and Generation
Some computer vision models are not only capable of analyzing but also generating images. In this case, the task is to create new images based on given conditions or predict future states of a scene. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), Diffusion Neural Networks, and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) are the main approaches in this area.
Computer vision has not only improved our ability to analyze and process visual data, but has also led to numerous revolutionary applications in various industries. Whether it's improving diagnostics in medicine, automating production processes, or ensuring road safety, computer vision plays a key role. Next, we will examine how these tasks are applied in real sectors.
Healthcare
One of the most significant applications of computer vision is in healthcare. Modern artificial intelligence models help doctors diagnose diseases more accurately.
Radiology: Algorithms can analyze medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, detecting anomalies with accuracy comparable to qualified doctors. This significantly speeds up the diagnostic process and allows for faster treatment.
Oncology: Computer vision models assist in detecting malignant tumors at early stages, especially in diagnostically challenging areas such as the lungs or the breast.
Telemedicine: In remote access conditions, computer vision algorithms can provide significant assistance by conducting initial analysis of images taken by patients and relaying the results to specialists for further review.
Commerce and Retail
Computer vision is actively used in commerce to enhance the shopping experience and optimize business processes.
Customer Analysis: Monitoring systems using cameras can analyze customer behavior in stores, helping to identify preferences and improve product placement.
Inventory Management: Automatic systems can track stock on shelves using visual recognition, allowing for timely replenishment of goods and improved warehouse management.
Self-Service Systems: Modern self-checkout kiosks use computer vision to recognize products and verify age restrictions, speeding up the purchasing process and reducing the need for service personnel.
Automotive Industry
The development of computer vision technologies plays a key role in creating safe and efficient vehicles.
Autonomous Vehicles: Computer vision is used to recognize road signs, pedestrians, other vehicles, and road conditions, enabling autonomous vehicles to move safely and reliably.
Driver Assistance: Driver assistance systems (ADAS) have been developed, using computer vision to prevent collisions, lane keeping, and automatic parking maneuvers.
Industry
In industrial sectors, computer vision contributes to automation and improved efficiency of manufacturing processes.
Quality Control: Artificial intelligence models can automatically detect defects on the production line, ensuring high product quality and minimizing losses.
Robotics: In industrial logistics, robots equipped with computer vision systems can efficiently navigate in space, transport materials and components, and interact with other machines.
Agriculture
Agriculture also greatly benefits from the application of computer vision.
Crop Management: Image analysis systems assist in monitoring crop growth, identifying plant pests and diseases, allowing agricultural producers to apply measures in a timely manner and optimize crop productivity.
Automation: Robots equipped with computer vision systems can automatically harvest crops, cut vegetables and fruits, increasing efficiency and reducing labor costs.
Safety and Monitoring
Computer vision is actively used in security and monitoring systems.
Facial Recognition: Facial recognition systems are used to increase security levels at facilities, enabling the identification of individuals in large crowds.
Video Analysis: Computer vision models are applied to analyze video materials in real-time, detecting suspicious behavior and preventing potential threats.
Conclusion
Modern computer vision models continue to expand their boundaries, finding application in an increasing number of economic sectors. These technologies not only enhance process efficiency and automation, but also make our lives safer and more comfortable. It is important to understand that the further development and implementation of these technologies will depend not only on scientific achievements, but also on international cooperation, legislation, and ethical aspects.
Jun 23, 2024